
Class for sorting of vectors. More...
#include <itpp/base/sort.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| Sort (SORTING_METHOD method=INTROSORT) | |
| Constructor that sets Intro Sort method by default. | |
| void | set_method (SORTING_METHOD method) |
| Set sorting method. | |
| SORTING_METHOD | get_method () const |
| Get current sorting method. | |
| void | sort (int low, int high, Vec< T > &data) |
| Sorting function of a subset of a vector data. | |
| ivec | sort_index (int low, int high, const Vec< T > &data) |
| Sorting function that returns a sorted index vector. | |
| void | intro_sort (int low, int high, int max_depth, Vec< T > &data) |
Introsort function of a subset of a vector data. | |
| ivec | intro_sort_index (int low, int high, int max_depth, const Vec< T > &data) |
| Introsort function, which returns a sorted index vector. | |
Class for sorting of vectors.
A class which takes a vector, and sorts its values descending. There are two types of sort: a normal sort (accessed via the Sort::sort() function) which sorts the vector passed in the argument, and an index sort (accessed via the Sort::sort_index() function) which leaves the passed vector intact, but returns an index vector describing the sorted order.
The Sort class has four sorting methods implemented:
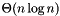 comparisons, bu has the efficiency of the quick sort algorithm in cases where the data is well conditioned for quicksort.
comparisons, bu has the efficiency of the quick sort algorithm in cases where the data is well conditioned for quicksort.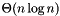 comparisons. For most data sets, the quicksort will be significantly more efficient than this average. However for data sets not well suited to it, quicksort may require as many as
comparisons. For most data sets, the quicksort will be significantly more efficient than this average. However for data sets not well suited to it, quicksort may require as many as 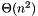 comparisons. Example of such ill-suited data sets are those which are nearly in order, and data sets with multiple elements of the same value.
comparisons. Example of such ill-suited data sets are those which are nearly in order, and data sets with multiple elements of the same value.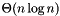 comparisons. This makes it an ideal quicksort replacement for data sets that that are ill-conditioned for quicksorting.
comparisons. This makes it an ideal quicksort replacement for data sets that that are ill-conditioned for quicksorting.References:
| void itpp::Sort< T >::sort | ( | int | low, |
| int | high, | ||
| Vec< T > & | data | ||
| ) |
Sorting function of a subset of a vector data.
| low | Start index of a subvector to be sorted |
| high | End index of a subvector to be sorted |
| data | Data vector, in which a part of it is to be sorted |
Definition at line 215 of file sort.h.
References itpp::Vec< Num_T >::_data(), it_assert, it_error, itpp::levels2bits(), and itpp::Vec< Num_T >::size().
| ivec itpp::Sort< T >::sort_index | ( | int | low, |
| int | high, | ||
| const Vec< T > & | data | ||
| ) |
Sorting function that returns a sorted index vector.
| low | Start index of a subvector to be sorted |
| high | End index of a subvector to be sorted |
| data | Data vector, in which a part of it is to be sorted |
Definition at line 245 of file sort.h.
References itpp::Vec< Num_T >::_data(), it_assert, it_error, itpp::levels2bits(), and itpp::Vec< Num_T >::size().
| void itpp::Sort< T >::intro_sort | ( | int | low, |
| int | high, | ||
| int | max_depth, | ||
| Vec< T > & | data | ||
| ) |
Introsort function of a subset of a vector data.
| low | Start index of a subvector to be sorted |
| high | End index of a subvector to be sorted |
| max_depth | Maximum recursion depth before switching to heap sort recommended value: log2 of the length of the data vector |
| data | Data vector, in which a part of it is to be sorted |
Definition at line 286 of file sort.h.
References itpp::Vec< Num_T >::_data(), it_assert, and itpp::Vec< Num_T >::size().
| ivec itpp::Sort< T >::intro_sort_index | ( | int | low, |
| int | high, | ||
| int | max_depth, | ||
| const Vec< T > & | data | ||
| ) |
Introsort function, which returns a sorted index vector.
| low | Start index of a subvector to be sorted |
| high | End index of a subvector to be sorted |
| max_depth | Maximum recursion depth before switching to heap sort recommended value: log2 of the length of the data vector |
| data | Data vector, in which a part of it is to be sorted |
Definition at line 295 of file sort.h.
References itpp::Vec< Num_T >::_data(), it_assert, and itpp::Vec< Num_T >::size().
Generated on Sat Jul 6 2013 10:54:31 for IT++ by Doxygen 1.8.2