
Multilateration class for 3D indoor localization More...
#include <itpp/comm/multilateration.h>
Public Types | |
| enum | Type { MULTI_FAILURE = -1, MULTI_SPHERICAL, MULTI_HYPERBOLIC, MULTI_HYBRID } |
| Multilateration types as detected from user input (method binary vector) More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| Multilateration () | |
| Multilateration class default constructor | |
| Multilateration (const itpp::bvec &method, const itpp::mat &bs_pos) | |
| Multilateration class constructor | |
| virtual | ~Multilateration () |
| Multilateration destructor | |
| void | setup (const itpp::bvec &method, const itpp::mat &bs_pos) |
| Setup function for specifying the multilateration method and the base station positions. | |
| bool | get_pos (itpp::vec &ms_pos, const itpp::vec &measures) |
| Computes the mobile station position for spherical and hybrid multilateration. | |
| bool | get_pos (itpp::vec &ms_pos, const itpp::mat &measures) |
| Computes the mobile station position for hyperbolic multilateration. | |
| unsigned int | get_nb_fails_part () const |
| Gets the number of failures of the partitioning algorithm used internally by the ML-estimator. | |
| unsigned int | get_nb_fails_pos () const |
| Gets the number of failures of the positioning algorithm used internally by the ML-estimator. | |
| void | reset_err_counters () |
| Resets the error counters (number of failures for the partitioning and positioning algorithms) | |
| Type | get_type () const |
| Gets the type of the multilateration method currently used by the ML-estimator. | |
| double | get_crlb (const vec &ms_pos, double sigma2) |
| Computes the Cramer Rao lower bound for the ML-estimator assuming the same noise variance for all measures. | |
Multilateration class for 3D indoor localization
Implements geometry-based methods for indoor localization:
In addition, it allows to compute the theoretical performance of the algorithm based on Cramer Rao Lower Bound (CRLB).
Geometry-based methods for indoor localization use several Base Stations (BSs), whose position is known, in order to compute the position of the Mobile Station (MS). By computing the distance to each BS (TOA ranging) or the difference between the distances to two BSs (TDOA) a system of non-linear equations is obtained that allows to compute the MS position. At least 4 measures (TOA or TDOA) are needed in order to obtain a determinate equation system. The algorithm implemented in this class can handle any number of measures (at least four) by using an asymptotic Maximum Likelihood (ML) estimator [1]. The input of the algorithm is represented by a method vector, specifying the type of each ranging measure (0 for TOA and 1 for TDOA), a matrix with BSs positions and a vector (for spherical and hybrid) or a matrix (for hyperbolic multilateration) with the ranging measures. The output is a vector of length 3 with the position of the MS in 3D cartezian coordinates.
Note that for hybrid multilateration the method vector should have at least a one and a zero, for spherical multilateration the method vector is all zeros, while for hyperbolic multilateration is all ones.
The CRLB is computed as the Euclidean distance between the estimated position of the MS and the true MS position. The noise variance is needed as input together with the true MS position. It is assumed that the noise affecting the measures has the same variance for all measures.
Usage example:
Reference: [1] Urruela, A. and Riba, J. - Novel closed-form ML position estimator for hyperbolic location, ICASSP'04
Definition at line 85 of file multilateration.h.
Multilateration types as detected from user input (method binary vector)
| MULTI_FAILURE |
the algorithm has failed |
| MULTI_SPHERICAL |
spherical multilateration |
| MULTI_HYPERBOLIC |
hyperbolic multilateration |
| MULTI_HYBRID |
hybrid multilateration |
Definition at line 89 of file multilateration.h.
|
inline |
Multilateration class constructor
The BS positions are specified as a matrix, each BS position can be specified on either rows or columns. The method vector specify the measure type: 0 for TOA or 1 for TDOA. For example, a vector with all zeros represents spherical multilateration, while a vector with all ones represents hyperbolic multilateration.
For spherical multilateration the number of BSs and the method length must be equal. For hybrid and hyperbolic multilateration the number of BSs must be the method length plus one.
| method | multilateration method |
| bs_pos | base station positions in 3D cartezian coordinates |
Definition at line 106 of file multilateration.h.
|
inline |
Setup function for specifying the multilateration method and the base station positions.
The BS positions are specified as a matrix, each BS position can be specified on either rows or columns. The method vector specify the measure type: O for TOA or 1 for TDOA. A vector with all zeros represents spherical multilateration, while a vector with all ones represents hyperbolic multilateration.
For spherical multilateration the number of BSs and the method lenght must be equal and it must also equal the length of the measures vector.
For hybrid and hyperbolic multilateration the number of BSs must be the method length plus one.
| method | multilateration method |
| bs_pos | base station positions |
Definition at line 124 of file multilateration.h.
References it_error.
|
inline |
Computes the mobile station position for spherical and hybrid multilateration.
For spherical multilateration the vector of measures should be generated as follows:
![\[ measures(i) = dist(bs\_pos(i), ms\_pos) \]](form_185.png)
where 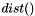 is the Euclidean distance between two points in 3D cartezian coordinates.
is the Euclidean distance between two points in 3D cartezian coordinates.
For hybrid multilateration the vector of measures is generated as:
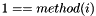 (TDOA ranging measure)
(TDOA ranging measure)
![\[ measures(i) = dist(bs\_pos(i+1), ms\_pos)-dist(bs\_pos(0), ms\_pos) \]](form_188.png)
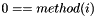 (TOA ranging measure)
(TOA ranging measure)
![\[ measures(i) = dist(bs\_pos(i), ms\_pos) \]](form_185.png)
| ms_pos | output with mobile station position in 3D cartezian coordinates |
| measures | vector with ranging measures |
Definition at line 142 of file multilateration.h.
|
inline |
Computes the mobile station position for hyperbolic multilateration.
The matrix of measures is computed as follows:
![\[ measures(i,j) = dist(bs\_pos(i), ms\_pos)-dist(bs\_pos(j), ms\_pos) \]](form_190.png)
where 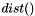 is the Euclidean distance between two points in 3D cartezian coordinates.
is the Euclidean distance between two points in 3D cartezian coordinates.
| ms_pos | output with mobile station position in 3D cartezian coordiates |
| measures | matrix with ranging measures |
Definition at line 152 of file multilateration.h.
| double itpp::Multilateration::get_crlb | ( | const vec & | ms_pos, |
| double | sigma2 | ||
| ) |
Computes the Cramer Rao lower bound for the ML-estimator assuming the same noise variance for all measures.
| ms_pos | true mobile station position |
| sigma2 | noise variance affecting the measures |
Definition at line 1514 of file multilateration.cpp.
References itpp::diag(), itpp::inv(), it_error, itpp::length(), itpp::sqrt(), itpp::sum(), and itpp::sum_sqr().
Generated on Sat May 25 2013 16:32:32 for IT++ by Doxygen 1.8.2